The NFS is a Robust, Easy to Manage Jurisdictional REDD+ Crediting Program
-
A focus on Natural Forests
-
Integration of social, biodiversity and carbon values
-
Limited to non-commercial forestry
-
Unified, risk-based performance benchmark to provide baselines
-
Suitable for medium and large-scale projects
Latest News

NFS ECO Appoints Northern Trust to Administer Natural Capital Credits
New Reference Level Methodology Under Consideration – open for public comment
The core mission of the NFS program is to deliver reliable finance to trustworthy ecological projects making a real and measurable difference in an efficient manner.
A Crediting Program that Integrates Social, Biodiversity and Carbon Values
Natural forests in many parts of the world are at risk of degradation and conversion to agriculture. Indeed, the annual CO2 emissions from deforestation in the tropics are similar in magnitude to the fossil fuel emissions from the European Union.
Historically, the main causes of forest loss have been the expansion of livestock and cropland along with often related activities such as unsustainable timber extraction and human-induced wildfires. In the future, climate change is expected to impact on forests through a combination of temperature extremes, rainfall changes and new pests.
Despite high-level commitments by governments to protect forests, the frequent reality on the ground is that additional resources are needed to secure protection and to begin the restoration of suitable areas.
The Natural Forest Standard (NFS) provides an efficient way of channelling finance to projects that address these threats. The Natural Capital Credits (NCCs) issued by the NFS represent 1 tCO2 avoided or removed through the protection and/or restoration of natural forest ecosystems.
NCCs are generated through a crediting process that is designed with the ICVCM’s Core Carbon Principles (CCPs) in mind. While several details of the CCPs are still to be fully explained in practical terms, the Natural Forest Standard supports the general approach and aims of this initiative.
If you are working to protect or restore natural forests that are at risk and want to know more about the NFS process, please navigate to the For Developers section of this website to find out more.
If you are interested in buying high quality carbon credits that combine carbon, biodiversity and social values, please look at the Natural Capital Credits section to find further details.
Why is the NFS Needed?
International finance to protect and restore forests at risk is currently channelled through multiple poorly co-ordinated initiatives. These efforts sometimes duplicate and often fail to reach to the local areas where they can make a genuine difference.
Public (donor) finance is mainly distributed through multilateral financial institutions who work with high level national agencies dealing with climate policy issues. While national REDD programs have made progress in understanding and monitoring the causes of forest loss they have rarely delivered the resources needed to address the underlying problems and have sometimes diverted local forest and natural resource departments from their core activities.
Private finance is increasingly channelled to a diverse array of local projects that aim to generate carbon credits to fund conservation and restoration actions at grass roots levels. While several of these projects have achieved promising results, they are difficult to scale to become impactful at a regional or national levels. Some of these projects have also faced difficulties in achieving durable organisational status and long-term carbon benefits.
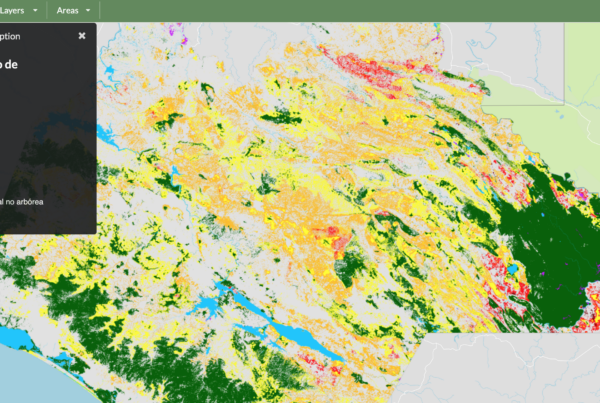
The Natural Forest Standard (NFS) fits as a building block between national scale initiatives and local projects. It provides a framework to quantify the risks to forests at regional levels, it identifies the resources needed at municipal, district, catchment or protected area scales to fill the gap between national programs and local projects, and it certifies the avoided emissions and removals from jurisdictional REDD+ programs.
Revenues from the sale of these Natural Capital Credits (NCCs) can be reinvested locally in forest and agricultural resilience and adaptation efforts.



